高效、低成本的XML数据绑定和代码生成XML加快了项目的上市时间
从XML schema生成构造良好、可靠类库的复杂性可能会挑战任何项目的时间表和人员生产力。XBinder XSD代码生成工具根据XML schema (XSD)文件自动将对象序列化为XML,并将XML反序列化为C、C++、Java或C#对象,从而大大简化了项目的开发和维护时间。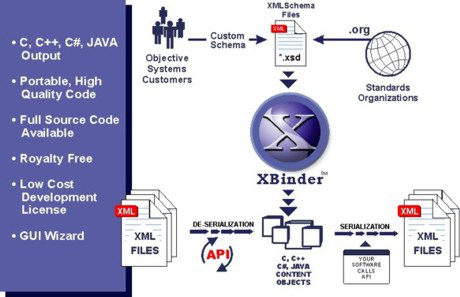
XBinder的特性现在包括了:
1. 组在XML Schema 1.1中包含重复元素和通配符的能力
2. 对于Linux,我们现在提供了用GCC 4、5和6编译的运行时库。
3.我们不再为GCC 3构建库。默认情况下,示例程序将使用GCC 4库。
为什么要使用XML数据绑定或XML代码生成工具?
与传统XML API(如SAX和DOM)相比,XBinder的XML数据绑定具有以下优点:
性能——使用XML模式生成的代码进行验证或(反)序列化等操作比使用验证解析器更快。
简单性——XBinder自动生成构造良好、易于阅读的代码,从而加快上市周期。
可靠性——XML数据绑定应用程序通过在模式级别工作来确保生成的XML文档的有效性。
XBinder的概述
XBinder是C/C++、Java或C#代码生成工具的XML模式。XML数据绑定(或代码生成)是将XML模式信息项转换为计算机语言中的类型定义和函数的过程。
XBinder代码生成工具生成的源代码是C、C++、Java或C#源代码,由类型定义和编码/解码函数组成。这为处理XML模式规范中包含的所有消息定义提供了一个完整的应用程序编程接口(API)。
除了代码生成器之外,程序包中还包含一个公共编码/解码函数的运行时库。这个库包含对基本XML模式简单类型(整数、字符串、hexBinary等)进行编码和解码的例程。XBinder代码生成工具组装了一系列对这些函数的调用,以完成对更复杂消息类型的编码或解码。
评估版本可用于Windows、Linux、各种UNIX平台和Apple Mac OSX。
对比
假设您需要编写代码来解析下面的XML实例,并打印出其中包含的所有数据。
<purchase>
<customer number="12345">
John Smith
</customer>
<store>
Toys R Us
</store>
<item>
Toy Bath Set
</item>
<price>
19.95
</price>
</purchase>
在这个页面上,我们将比较在没有XBinder的情况下解析这个实例所需的代码量与使用XBinder进行解析所需的代码量。这两个例子都将使用C++。对于非XBinder代码,我们将使用libxml++的DOM功能。下面是不使用XBinder时需要编写的代码:
#include <libxml++/libxml++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Parse the XML file.
xmlpp::DomParser parser;
parser.set_substitute_entities();
try
{
parser.parse_file("purchase.xml");
}
catch (std::exception& ex)
{
printf("\n%s", ex.what());
}
// Get the root node.
xmlpp::Node* pPurchaseNode = parser.get_document()->get_root_node();
Glib::ustring nodename = pPurchaseNode->get_name();
// Get the root node's children in a list.
xmlpp::Node::NodeList purchaseChildren = pPurchaseNode->get_children();
// Now walk through the children and process them according to what element
// is represented.
for (xmlpp::Node::NodeList::iterator iter = purchaseChildren.begin();
iter != purchaseChildren.end(); ++iter)
{
xmlpp::Node* pChildNode = *iter;
nodename = pChildNode->get_name();
if (nodename == "text")
{
// We'll get the text value for each element explicitly
// as we encounter them.
continue;
}
else if (nodename == "customer")
{
// We're at the <customer> node. We want to print the customer
// name and number.
xmlpp::Element* pChildElement =
dynamic_cast<xmlpp::Element*> (pChildNode);
xmlpp::Attribute* pCustomerAttr =
pChildElement->get_attribute("number");
printf("\nCustomer number: %s", pCustomerAttr->get_value().c_str());
xmlpp::TextNode* pChildText = pChildElement->get_child_text();
printf("\nCustomer name: %s", pChildText->get_content().c_str());
}
else if (nodename == "store")
{
// We're at the <store> node. We want to print the store name.
xmlpp::Element* pChildElement =
dynamic_cast<xmlpp::Element*> (pChildNode);
xmlpp::TextNode* pChildText = pChildElement->get_child_text();
printf("\nStore name: %s", pChildText->get_content().c_str());
}
else if (nodename == "item")
{
// We're at the <item> node. We want to print the item name.
xmlpp::Element* pChildElement =
dynamic_cast<xmlpp::Element*> (pChildNode);
xmlpp::TextNode* pChildText = pChildElement->get_child_text();
printf("\nItem name: %s", pChildText->get_content().c_str());
}
else if (nodename == "price")
{
// We're at the <price> node. We want to print the price.
xmlpp::Element* pChildElement =
dynamic_cast<xmlpp::Element*> (pChildNode);
xmlpp::TextNode* pChildText = pChildElement->get_child_text();
printf("\nPrice: %s", pChildText->get_content().c_str());
}
}
return 0;
}
下面是需要使用XBinder编写的代码:
#include "rtxsrc/OSRTFileInputStream.h"
#include "rtxmlsrc/rtXmlCppMsgBuf.h"
#include <Purchase.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Setup to decode the instance in purchase.xml
int stat;
const char* filename = "Purchase.xml";
OSRTFileInputStream in (filename);
OSXMLDecodeBuffer decodeBuffer (in);
purchase_CC pdu (decodeBuffer);
// Do the decode
stat = pdu.decode();
// Print the information that was in the instance.
PurchaseRecord* pPurchase = pdu.getValue();
printf("\nCustomer number: %d", pPurchase->customer.number);
printf("\nCustomer name: %s", pPurchase->customer.value.c_str());
printf("\nStore name: %s", pPurchase->store.c_str());
PurchaseRecord_3* pItemAndPrice = pPurchase->_seq3.getItem(0);
unsigned short i = 0;
while (pItemAndPrice != 0)
{
printf("\nItem name: %s", pItemAndPrice->item.c_str());
printf("\nItem price: %.2f", pItemAndPrice->price);
pItemAndPrice = pPurchase->_seq3.getItem(++i);
}
return stat;
}
关于这些代码示例,有几点值得注意: